現在の投稿数 177
【 Python Data Structures and Algorithms 】Python とデータ構造 ( data structure ) - linked list を実装してみよう! Linked List 実装 Python Programming Interview 模擬問題 投稿一覧へ戻る
Published 2020年8月1日12:33 by mootaro23
SUPPORT UKRAINE
- Your indifference to the act of cruelty can thrive rogue nations like Russia -
プログラム開発をする上で、データ構造 ( data structure ) とアルゴリズム ( algorithm ) の知識は必須です。
そこで今回は Linked List を実装してみます。
Linked List は要素 ( ノード: node ) のただの羅列に過ぎません。
しかし、それぞれのノードは、自分の次に並んでいるノードの情報を持っています。
ですから、Linked List の実装には、Node クラスと、それらを管理して Linked List としての機能を提供するクラスの2つが必要です。
是非 Python 用の Programming Interview の前哨戦として挑戦してみてください。
制限時間: 60分
Question:
各ステートメントを実行した際には、print 文によって以下の内容が表示されるか、メッセージが表示されること。
解答例は こちら
そこで今回は Linked List を実装してみます。
Linked List は要素 ( ノード: node ) のただの羅列に過ぎません。
しかし、それぞれのノードは、自分の次に並んでいるノードの情報を持っています。
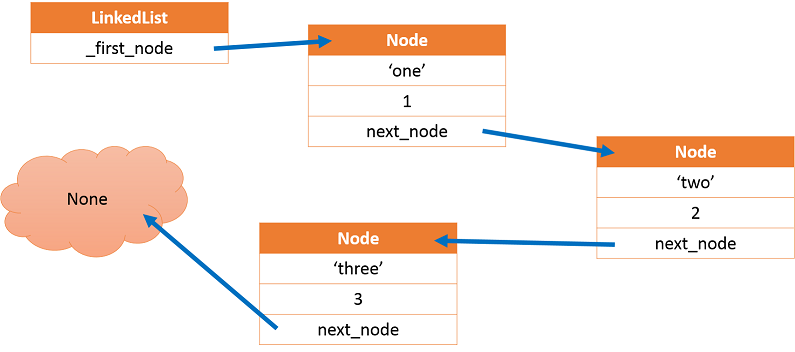
ですから、Linked List の実装には、Node クラスと、それらを管理して Linked List としての機能を提供するクラスの2つが必要です。
是非 Python 用の Programming Interview の前哨戦として挑戦してみてください。
制限時間: 60分
Question:
・以下の Node クラスのインスタンスを要素とする linked list を実装してください。
・必要なクラスは Node クラスと Linkedlist クラスの2つですが、Node クラスは与えられているものをそのまま使用してください。
・LinkedList クラスではすでに __init__ と __repr__ が実装されています。この2つの関数は変更せずにこのまま使用してください。
・LinkedList クラスで実装が必要な関数の定義は与えられています。それらの関数の実体をコーディングしてください。
・それぞれの関数を使用した際の出力結果が、与えられている出力結果と一致していなければなりません。
class Node:
"""
注意: このクラスは変更せずこのまま使用すること。
Linked List を構成する要素 ( ノード )。
"""
def __init__(self, name: str, age: int):
"""
:attribute next_node: 自分の次に位置するノード ( Node 型 )。自分が最後の場合は None 。
"""
self.name = name
self.age = age
self.next_node = None
def __repr__(self):
return f"{self.name}({self.age})"
class LinkedList:
"""
Linked List 実装クラス
"""
def __init__(self, first_node: Node = None):
"""
注意: この関数は変更せずこのまま使用すること。
:param first_node: Linked List の最初のノード ( Node 型 )。
"""
self._first_node = first_node
def __repr__(self):
"""
注意: この関数は変更せずこのまま使用すること。
"""
nodes = []
node = self._first_node
while node is not None:
nodes.append(repr(node))
node = node.next_node
nodes.append('None')
return ' -> '.join(nodes)
def __len__(self):
"""
:return: int型
"""
pass
def prepend(self, other: Node):
"""
リストの先頭にノードを追加する。
:param other: 追加するノード
"""
pass
def append(self, other: Node):
"""
リストの最後にノードを追加する。
:param other: 追加するノード
"""
pass
def append_after(self, arg_name: str, other: Node):
"""
name 属性値として arg_name を持つノードの後に other を追加する。
arg_name を持つノードが存在しない場合はメッセージを表示し終了する(追加しない)。
同じ属性値を持つノードがリストに複数含まれている場合は、先頭から検索し最初にマッチしたノードの次に追加する。
:param arg_name: この値の name 属性を持つノードの後に追加する
:param other: 追加するノード
"""
pass
def find_node(self, arg_name: str):
"""
name 属性値として arg_name を持つノードを検索する。
同じ属性値を持つノードがリストに複数含まれている場合は、先頭から検索し最初にマッチしたノードを返す。
:param arg_name: この値の name 属性を持つノードを検索する
:return: 該当するノード、もしくは、None (見つからなかった場合)
"""
pass
def remove(self, arg_name: str):
"""
name 属性値として arg_name を持つノードを削除する。
同じ属性値を持つノードがリストに複数含まれている場合は、先頭から検索し最初にマッチしたノードを削除する。
:param arg_name: この値の name 属性値を持つノードを削除する
"""
pass
def reverse(self):
"""
Linked list の並び順を逆にする。
"""
pass
def reverse_recursive(self):
"""
reverse 関数の再帰バージョン
"""
def recursion(cur, prev):
pass
self._first_node = recursion(cur=self._first_node, prev=None)
"""
注意: このクラスは変更せずこのまま使用すること。
Linked List を構成する要素 ( ノード )。
"""
def __init__(self, name: str, age: int):
"""
:attribute next_node: 自分の次に位置するノード ( Node 型 )。自分が最後の場合は None 。
"""
self.name = name
self.age = age
self.next_node = None
def __repr__(self):
return f"{self.name}({self.age})"
class LinkedList:
"""
Linked List 実装クラス
"""
def __init__(self, first_node: Node = None):
"""
注意: この関数は変更せずこのまま使用すること。
:param first_node: Linked List の最初のノード ( Node 型 )。
"""
self._first_node = first_node
def __repr__(self):
"""
注意: この関数は変更せずこのまま使用すること。
"""
nodes = []
node = self._first_node
while node is not None:
nodes.append(repr(node))
node = node.next_node
nodes.append('None')
return ' -> '.join(nodes)
def __len__(self):
"""
:return: int型
"""
pass
def prepend(self, other: Node):
"""
リストの先頭にノードを追加する。
:param other: 追加するノード
"""
pass
def append(self, other: Node):
"""
リストの最後にノードを追加する。
:param other: 追加するノード
"""
pass
def append_after(self, arg_name: str, other: Node):
"""
name 属性値として arg_name を持つノードの後に other を追加する。
arg_name を持つノードが存在しない場合はメッセージを表示し終了する(追加しない)。
同じ属性値を持つノードがリストに複数含まれている場合は、先頭から検索し最初にマッチしたノードの次に追加する。
:param arg_name: この値の name 属性を持つノードの後に追加する
:param other: 追加するノード
"""
pass
def find_node(self, arg_name: str):
"""
name 属性値として arg_name を持つノードを検索する。
同じ属性値を持つノードがリストに複数含まれている場合は、先頭から検索し最初にマッチしたノードを返す。
:param arg_name: この値の name 属性を持つノードを検索する
:return: 該当するノード、もしくは、None (見つからなかった場合)
"""
pass
def remove(self, arg_name: str):
"""
name 属性値として arg_name を持つノードを削除する。
同じ属性値を持つノードがリストに複数含まれている場合は、先頭から検索し最初にマッチしたノードを削除する。
:param arg_name: この値の name 属性値を持つノードを削除する
"""
pass
def reverse(self):
"""
Linked list の並び順を逆にする。
"""
pass
def reverse_recursive(self):
"""
reverse 関数の再帰バージョン
"""
def recursion(cur, prev):
pass
self._first_node = recursion(cur=self._first_node, prev=None)
各ステートメントを実行した際には、print 文によって以下の内容が表示されるか、メッセージが表示されること。
linked_list = LinkedList()
print(linked_list)
# None
linked_list.remove('nothing')
# リストは空です
linked_list.append(Node('two', 2))
linked_list.append(Node('three', 3))
print(linked_list)
# two(2) -> three(3) -> None
linked_list.prepend(Node('one', 1))
print(linked_list)
# one(1) -> two(2) -> three(3) -> None
linked_list.append(Node('four', 4))
linked_list.append(Node('five', 5))
linked_list.append(Node('seven', 7))
print(linked_list)
# one(1) -> two(2) -> three(3) -> four(4) -> five(5) -> seven(7) -> None
linked_list.append_after('five', Node('six', 6))
print(linked_list)
# one(1) -> two(2) -> three(3) -> four(4) -> five(5) -> six(6) -> seven(7) -> None
linked_list.reverse()
print(linked_list)
# seven(7) -> six(6) -> five(5) -> four(4) -> three(3) -> two(2) -> one(1) -> None
linked_list.reverse_recursive()
print(linked_list)
# one(1) -> two(2) -> three(3) -> four(4) -> five(5) -> six(6) -> seven(7) -> None
linked_list.remove('nothing')
# リスト内に名前は存在しません (nothing)。0 個のノードが削除されました。
linked_list.remove('one')
print(linked_list)
# two(2) -> three(3) -> four(4) -> five(5) -> six(6) -> seven(7) -> None
linked_list.remove('four')
print(linked_list)
# two(2) -> three(3) -> five(5) -> six(6) -> seven(7) -> None
linked_list.remove('seven')
print(linked_list)
# two(2) -> three(3) -> five(5) -> six(6) -> None
print(len(linked_list))
# 4
print(linked_list.find_node('three'))
# three(3)
print(linked_list.find_node('ten'))
# None
print(linked_list)
# None
linked_list.remove('nothing')
# リストは空です
linked_list.append(Node('two', 2))
linked_list.append(Node('three', 3))
print(linked_list)
# two(2) -> three(3) -> None
linked_list.prepend(Node('one', 1))
print(linked_list)
# one(1) -> two(2) -> three(3) -> None
linked_list.append(Node('four', 4))
linked_list.append(Node('five', 5))
linked_list.append(Node('seven', 7))
print(linked_list)
# one(1) -> two(2) -> three(3) -> four(4) -> five(5) -> seven(7) -> None
linked_list.append_after('five', Node('six', 6))
print(linked_list)
# one(1) -> two(2) -> three(3) -> four(4) -> five(5) -> six(6) -> seven(7) -> None
linked_list.reverse()
print(linked_list)
# seven(7) -> six(6) -> five(5) -> four(4) -> three(3) -> two(2) -> one(1) -> None
linked_list.reverse_recursive()
print(linked_list)
# one(1) -> two(2) -> three(3) -> four(4) -> five(5) -> six(6) -> seven(7) -> None
linked_list.remove('nothing')
# リスト内に名前は存在しません (nothing)。0 個のノードが削除されました。
linked_list.remove('one')
print(linked_list)
# two(2) -> three(3) -> four(4) -> five(5) -> six(6) -> seven(7) -> None
linked_list.remove('four')
print(linked_list)
# two(2) -> three(3) -> five(5) -> six(6) -> seven(7) -> None
linked_list.remove('seven')
print(linked_list)
# two(2) -> three(3) -> five(5) -> six(6) -> None
print(len(linked_list))
# 4
print(linked_list.find_node('three'))
# three(3)
print(linked_list.find_node('ten'))
# None
解答例は こちら
この記事に興味のある方は次の記事にも関心を持っているようです...
- People who read this article may also be interested in following articles ... -
