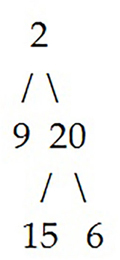Python Coding Challenge - How will you find the maximum height of a binary tree?
(Python コーディングチャレンジ [バイナリツリーの最大高を求めよう!] 編)
(Python コーディングチャレンジ [バイナリツリーの最大高を求めよう!] 編)
今回の問題も DFS アルゴリズムを利用することで簡単に解決することができます。
問題:
与えられたバイナリツリーの最大の高さを求めるプログラムを記述してください。この問題における「最大の高さ」とは、ルートノードから末端のリーフノード (leaf nodes) に至るパスのうち、最も多くのノードを含むパスのノード数とします (「ツリーの高さ」といった場合、一般的には最も長いパスに含まれる edges の数を指します)。
例:
例として配列; root [2, 9, 20, None, None, 15, 6] で表現されるバイナリツリーを考えます:
与えられるバイナリツリー: root
# 出力: 3
例の解説:
このツリーにおける最長パスは「2-20-15」か「2-20-6」のいずれかです。この時これらのパスに含まれるノードの数は 3 ですからその数を返します。
また関数定義は以下のような形です (同じである必要はありません):
from typing import Optional
def max_depth(root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
...
def max_depth(root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
...
また TreeNode クラスは「Python coding challenge の前準備: Basics of Graph Theory Part.3 - Representation and Manipulation of Trees (グラフ理論の基礎総復習 その3 - ツリーの表現と操作)」で定義した次のクラスを利用します:
from typing import Optional, Any
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, v: Any):
self.val = v
self.left: Optional[TreeNode] = None
self.right: Optional[TreeNode] = None
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, v: Any):
self.val = v
self.left: Optional[TreeNode] = None
self.right: Optional[TreeNode] = None
作成したプログラムは以下のテストをパスする必要があります:
from typing import Optional
import unittest
def make_tree(arr: list[Optional[int]], root: Optional[TreeNode] = None, index: int = 0) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if index < len(arr):
root = TreeNode(arr[index])
root.left = make_tree(arr, root.left, index * 2 + 1)
root.right = make_tree(arr, root.right, index * 2 + 2)
return root
class TestMaxDepth(unittest.TestCase):
def test_1(self):
arr = []
root = make_tree(arr)
res = max_depth(root)
self.assertEqual(res, 0)
def test_2(self):
arr = [1]
root = make_tree(arr)
res = max_depth(root)
self.assertEqual(res, 1)
def test_3(self):
arr = [2, 9, 20, None, None, 15, 6]
root = make_tree(arr)
res = max_depth(root)
self.assertEqual(res, 3)
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
import unittest
def make_tree(arr: list[Optional[int]], root: Optional[TreeNode] = None, index: int = 0) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if index < len(arr):
root = TreeNode(arr[index])
root.left = make_tree(arr, root.left, index * 2 + 1)
root.right = make_tree(arr, root.right, index * 2 + 2)
return root
class TestMaxDepth(unittest.TestCase):
def test_1(self):
arr = []
root = make_tree(arr)
res = max_depth(root)
self.assertEqual(res, 0)
def test_2(self):
arr = [1]
root = make_tree(arr)
res = max_depth(root)
self.assertEqual(res, 1)
def test_3(self):
arr = [2, 9, 20, None, None, 15, 6]
root = make_tree(arr)
res = max_depth(root)
self.assertEqual(res, 3)
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
考え方:
この問題の解決方法としては再帰処理を利用するのが最も効率的でしょう。上の例で考えます。ルートノードとして 2 が与えれらた場合、そのノードの高さは 2 の子ノードである 9 もしくは 20 の高さに 1 を加えたもの、と考えることができます。つまり、リーフノードからルートノードに向かって「高さ」を考えていくことになります。
この処理を再帰的に行う関数 max_depth() を実装しパラメータとして root を渡します。この再帰動作の base case は、渡されてきたノード自体が None である時 (この階層の「高さ」は存在しませんから 0 を返します)と、渡されてきたノードがリーフノード、つまり left / right 双方の子ノードが存在しない時 (この階層自体の高さ 1 を返します) です。
それ以外の場合は自分の left 子ノード、もしくは、right 子ノードを引数として自分自身を実行し、返ってきた値 (子ノードの高さ) の大きい方に自分の階層の高さ 1 を加えて呼び出し元に返します。
プログラム実装例:
from typing import Optional
def max_depth(root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
if (not root.left) and (not root.right):
return 1
left_h = max_depth(root.left)
right_h = max_depth(root.right)
return max(left_h, right_h) + 1
def max_depth(root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
if (not root.left) and (not root.right):
return 1
left_h = max_depth(root.left)
right_h = max_depth(root.right)
return max(left_h, right_h) + 1
Complexity Analysis
(アルゴリズム解析)
Time complexity (実行計算時間):
渡されたバイナリツリーを1度だけ走査していますから O(n) です。
Space complexity (実行メモリ要求量):
再帰呼び出しの回数は渡されたバイナリツリーの「高さ (h)」に依存します。またノード数が n のバイナリツリーの最大高さは n ですから O(n) です。